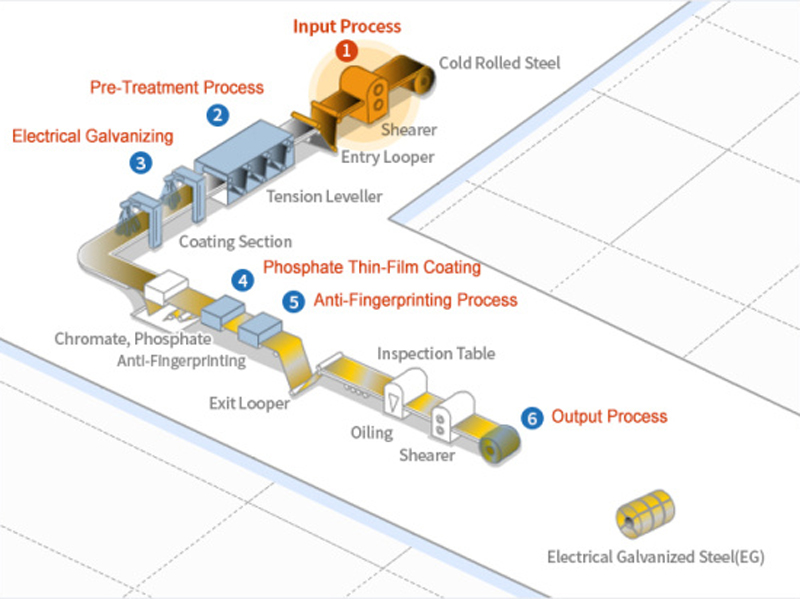
Electrical Galvanized Steel Production Process Introduction
1. Input process: The input point of the electrogalvanizing wire is equipped with a pay-off reel, a shearing machine, a welding machine, a looper, and a tension and straightening machine. Pay-off reels transport stacked or cold-rolled steel to shears, which cut and join them in preparation for welding. Next comes the welding process.
2. Pre-treatment process: Electrolytic cleaning line, consisting of an electrolytic tank, acid bath, and rinsing tank, is used to remove contaminants and oxide films on the surface of steel before electroplating.
3. Electroplating: The CAROSEL method, as well as other electrogalvanizing techniques, involves plating one side at a time using a conductor roller. This process can produce double-sided, single-sided or different-sided electroplated plates. Additionally, the horizontal method allows both sides of the sheet to be plated simultaneously, resulting in a double-sided plated sheet.
4. Phosphate Film Coating: A phosphate film is applied to the surface of the zinc layer through a chemical or electrochemical reaction. The film provides temporary corrosion protection and provides a safe substrate for painting.
5. Anti-fingerprint process: Organic, inorganic or organic-inorganic hybrid films are applied to the surface of steel plates to enhance corrosion resistance and impart desired properties, such as resistance to fingerprint marks and improved processability.
6. Output process: The exit of the production line includes output loopers, tension reels and automatic packaging lines to protect the products after coil winding.
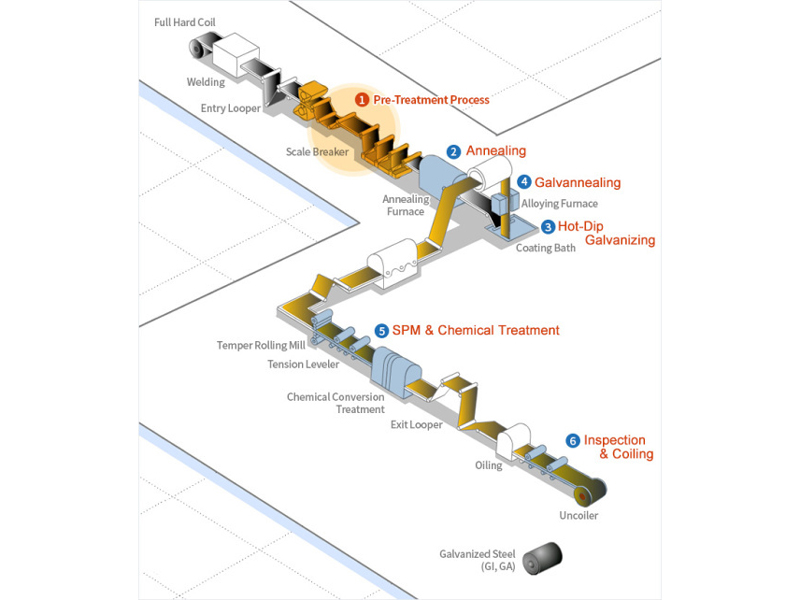
Galvanized Steel Process Introduction Diagram
1. Surface treatment: After cold-rolled steel plate processing, the charged steel plate is passed through an alkaline solution, triggering an electrochemical reaction to remove residual rolling oil and other contaminants, thereby cleaning the surface.
2. Annealing: The material properties of pre-treated steel plates are modified and enhanced by recrystallization during the annealing process.
3. Hot-dip galvanizing: After the annealing furnace, the steel plate is immersed in a zinc pot and the surface is covered with molten zinc. The desired coating weight is achieved by using high-pressure air in an air knife to remove excess zinc before curing.
4. Galvanized Annealing: After air knife treatment, the surface of the steel plate can be coated with zinc compounds and then reheated during the annealing process. This allows zinc atoms to diffuse into the iron, forming a zinc-iron alloy.
5. Surface Treatment and Coating: In order to obtain a smooth surface and exquisite finish, the steel plate is machined flat. In addition, in order to prevent the formation of white rust on the surface of active zinc and enhance corrosion resistance, the surface is coated with chromium-free resin.
6. Inspection and Coiling: Steel plates are thoroughly inspected and coiled to ensure quality and prepare them for further processing.

 Angle Steel
Angle Steel Channel Steel
Channel Steel Universal Beam (l-Beam)
Universal Beam (l-Beam) H-Beam Steel
H-Beam Steel Galvalume Steel Coil
Galvalume Steel Coil Galvalume Steel Sheet
Galvalume Steel Sheet Galvanized Steel Sheet
Galvanized Steel Sheet Color Coated Plate
Color Coated Plate Stainless Steel Bar
Stainless Steel Bar Stainless Steel Pipe
Stainless Steel Pipe Steel Bar
Steel Bar Wire Rope
Wire Rope Carbon Steel Pipe
Carbon Steel Pipe Carbon Steel Plate
Carbon Steel Plate Aluminum Plate
Aluminum Plate Aluminum Coil
Aluminum Coil Aluminum Pipe
Aluminum Pipe Aluminum Bar
Aluminum Bar Magnesium Ingot
Magnesium Ingot Fasteners
Fasteners
