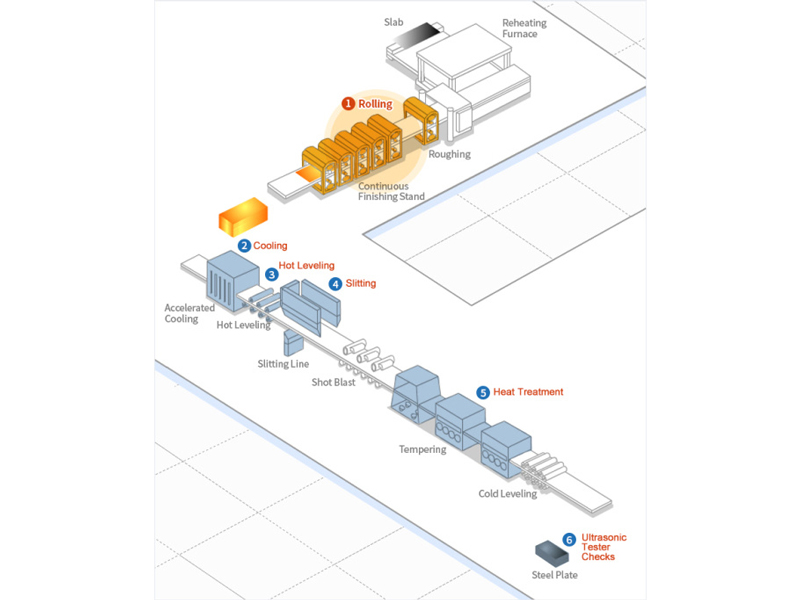
Steel Plate Production Process Introduction Diagram
1. Rolling: Our 4-high reversible finishing mill, with a maximum load of 7000 tons, ensures minimal internal defects even in thick plates. The implementation of automatic gauge control and shape control systems not only reduces thickness deviation but also enhances plate flatness, ensuring superior quality.
2. Cooling: Our advanced cooling system enables the production of high-strength steel without the need for heat treatment, achieved through rolling and accelerated cooling. Utilizing the mist cooling method with a suction type, our system boasts high cooling capacity and maintains a uniform temperature gradient in the widthwise direction, effectively reducing plate quality deviation.
3. Hot Leveling: The hot leveler is instrumental in producing superior quality flat plates by eliminating residual stress left on rolled plates, ensuring exceptional flatness and uniformity.
4. Slitting: Following the cooling process, the plates undergo meticulous dimensional accuracy inspection and are then cut into the appropriate width and length based on plate grade and thickness. This is carried out using either a mechanical shearing machine or flame planner, with production conditions tailored to factors such as the air knife gap and the nozzle size of the gas torch to achieve a higher degree of dimensional accuracy.
5. Heat Treatment: To meet the structural demands of our customers, plates undergo heat treatment after scale removal by shot blasters. Our non-oxidizing radiation tube type heat treating facilities produce scale-free heat-treated plates, ensuring the desired plate structure.
6. Ultrasonic Tester Checks: Our ultrasonic tester meticulously checks for blow holes, pipes, laminations, and other internal defects to guarantee the internal quality of plates demanded by our customers, ensuring the highest standards of quality and reliability.
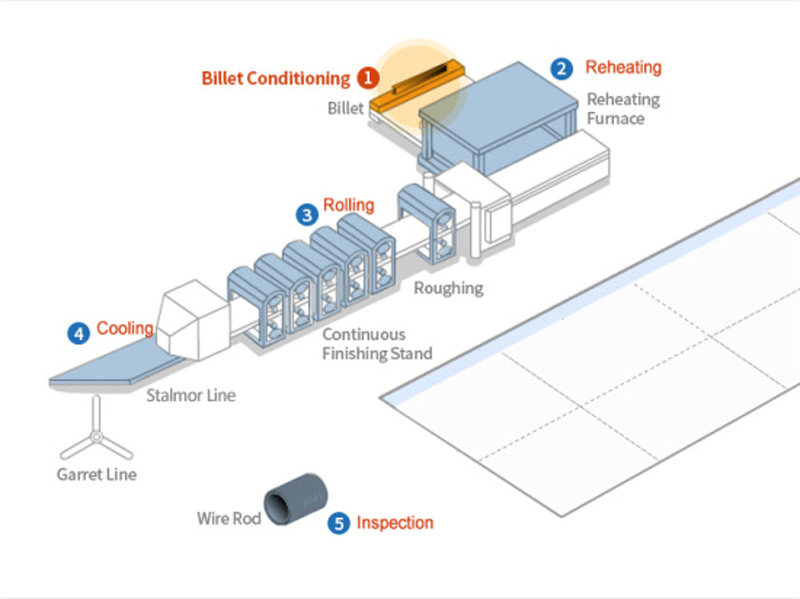
Wire Rod Production Process Introduction Diagram
1. Billet Conditioning: This important process involves a thorough inspection of the surface quality of the billet and removal of any defects. Shot peening is used to remove surface scale, while magnetic particle testing and visual inspection help identify and resolve defects using a grinder. In addition, ultrasonic testing as well as dimensional and geometric inspections are an integral part of the internal quality assurance process.
2. Reheating: The temperature and duration of furnace reheating are customized based on the specific application of the product. To prevent decarburization from affecting surface quality, the billet is preheated at a controlled low temperature before entering the heating furnace. To achieve this, the ratio of fuel to air needs to be tightly controlled.
3. Rolling: Accurately control the temperature, draft force, and deformation speed during the rolling process to meet customer requirements for material performance. Other measures to ensure surface quality include adjusting roll roughness and gaps, detecting cracks and correcting dimensions.
4. Cooling: The coiling temperature of the spinning machine, the air flow and moving speed of the cooling bed fan, and the cooling speed of the insulation cover are all carefully controlled to ensure that the product meets various specifications. application. High carbon steel wire rod is cooled quickly to obtain the microstructure required for successful drawing, while low carbon steel is cooled slowly to provide the softness required by the customer, eliminating the need for an annealing process.
5. Inspection: Samples are taken from the front and rear edges of the product after rolling and cooling for testing to identify defects in size, surface, or material integrity. In addition, packaging and labels are inspected according to customer requirements before shipment.
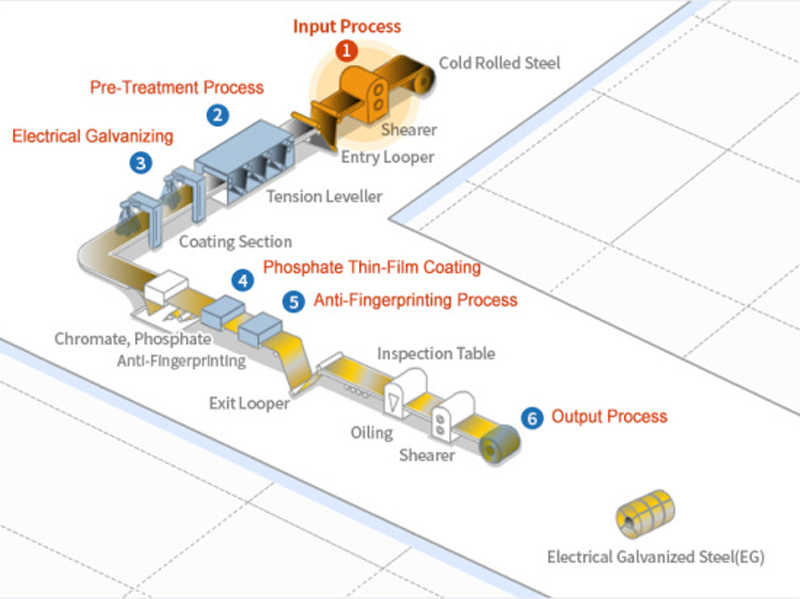
Electrical Galvanized Steels Production Process Introduction
1. Input Process: The entry point of the electrogalvanizing line is equipped with a pay-off reel, a shearing M/C, a welding M/C, a looper, and a tension leveler. The pay-off reel transports stacked or cold rolled steel materials to the shearing machine, which cuts and connects them in preparation for welding, followed by the welding process.
2. Pre-Treatment Process: An electrolytic cleaning line comprises an electrolysis tank, an acid bath, and a rinse tank to effectively remove contaminants and oxide films from the surface of the steel before electroplating, ensuring a clean and suitable surface for the subsequent processes.
3. Electrical Galvanizing: The CAROSEL method, along with other electric galvanizing techniques, involves the plating of one side at a time using a conductor roll. This process results in two-sided, single-sided, or differential-sided plated sheets. Additionally, the horizontal type allows for simultaneous plating of both sides of a sheet, producing a two-sided plated sheet.
4. Phosphate Thin-Film Coating: A phosphate thin-film is applied to the surface of the zinc layer through chemical or electrochemical reactions, providing temporary anti-corrosion protection and creating a secure painting substrate.
5. Anti-Fingerprinting Process: An organic, inorganic, or organic-inorganic hybrid film is applied to the surface of sheet steel to enhance corrosion resistance and desirable properties such as resistance to fingerprint marks and improved workability.
6. Output Process: The exit point of the line includes an output looper, tension reel, and an automatic packaging line to protect the products after coil winding, ensuring the safe and secure handling of the finished products.
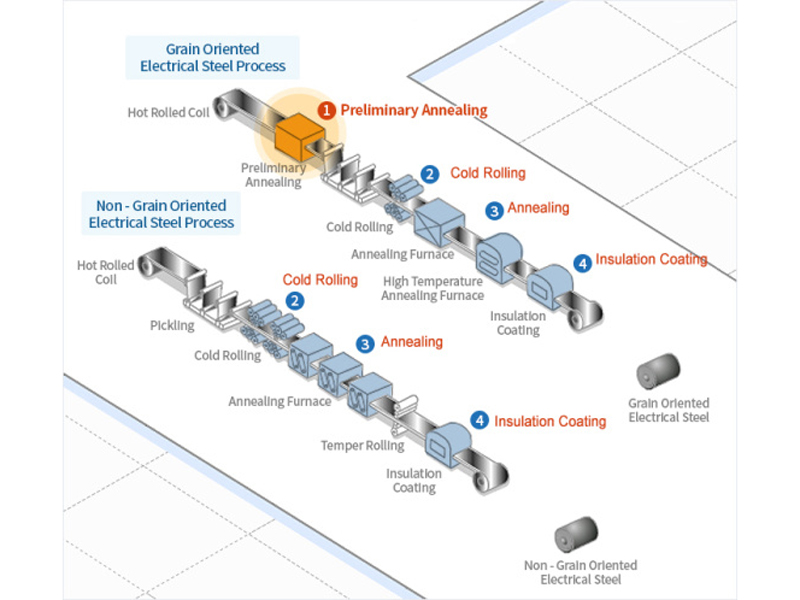
Electrical Eteel Production Process Introduction Diagram
1. Preliminary Annealing: During the preliminary annealing process, any scale formed on the hot rolled steel is effectively removed through delayed passing through a scale breaker and a hydrochloric acid bath. This initial heat treatment process not only enhances the cold rolling properties of the steel but also improves its magnetic properties.
2. Cold Rolling: To achieve specific thickness and material properties, a reduction ratio of 40-90% is typically applied. Rolling and edge trimming machines are automatically controlled to ensure uniform thickness and width.
3. Annealing: Annealing involves the transformation of cold rolled structures into a recrystallized structure through heat treatment. For grain oriented electrical steel, two distinct annealing methods are available: decarbonization annealing and high-temperature annealing. Decarbonization annealing removes excess carbon from the steel and applies a MgO coating, while high-temperature annealing produces secondary recrystallized structures with superior magnetic properties.
4. Insulation Coating: In this process, insulation coating is applied using a continuous coater roll to minimize eddy current losses, which are proportional to the sheet thickness. Multiple coaters are utilized to apply insulation coating liquid to both the top and bottom of the plate. Grain oriented electrical steel features a base coating of dark brown Forsterite (Mg2SiO4) and a transparent insulating coating containing phosphates, while non-oriented electrical steel employs various coating methods with different thicknesses and ingredients based on end usage and specific user requirements.

 Angle Steel
Angle Steel Channel Steel
Channel Steel Universal Beam (l-Beam)
Universal Beam (l-Beam) H-Beam Steel
H-Beam Steel Galvalume Steel Coil
Galvalume Steel Coil Galvalume Steel Sheet
Galvalume Steel Sheet Galvanized Steel Sheet
Galvanized Steel Sheet Color Coated Plate
Color Coated Plate Stainless Steel Bar
Stainless Steel Bar Stainless Steel Pipe
Stainless Steel Pipe Steel Bar
Steel Bar Wire Rope
Wire Rope Carbon Steel Pipe
Carbon Steel Pipe Carbon Steel Plate
Carbon Steel Plate Aluminum Plate
Aluminum Plate Aluminum Coil
Aluminum Coil Aluminum Pipe
Aluminum Pipe Aluminum Bar
Aluminum Bar Magnesium Ingot
Magnesium Ingot Fasteners
Fasteners
