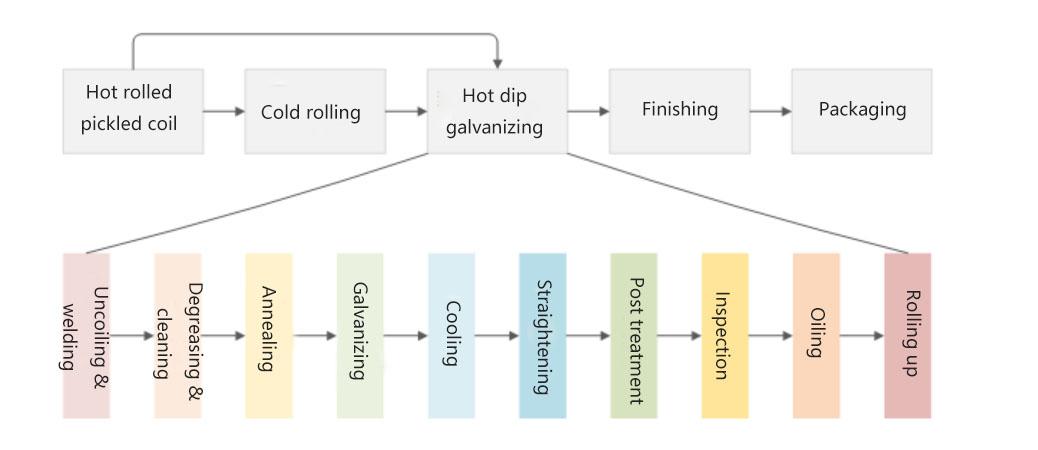
Electrical Eteel Production Process Introduction Diagram
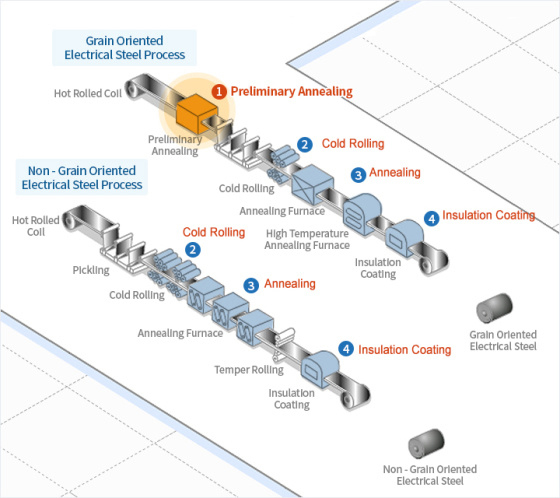
1. Preliminary Annealing: During the preliminary annealing process, any scale formed on the hot rolled steel is effectively removed through delayed passing through a scale breaker and a hydrochloric acid bath. This initial heat treatment process not only enhances the cold rolling properties of the steel but also improves its magnetic properties.
2. Cold Rolling: To achieve specific thickness and material properties, a reduction ratio of 40-90% is typically applied. Rolling and edge trimming machines are automatically controlled to ensure uniform thickness and width.
3. Annealing: Annealing involves the transformation of cold rolled structures into a recrystallized structure through heat treatment. For grain oriented electrical steel, two distinct annealing methods are available: decarbonization annealing and high-temperature annealing. Decarbonization annealing removes excess carbon from the steel and applies a MgO coating, while high-temperature annealing produces secondary recrystallized structures with superior magnetic properties.
4. Insulation Coating: In this process, insulation coating is applied using a continuous coater roll to minimize eddy current losses, which are proportional to the sheet thickness. Multiple coaters are utilized to apply insulation coating liquid to both the top and bottom of the plate. Grain oriented electrical steel features a base coating of dark brown Forsterite (Mg2SiO4) and a transparent insulating coating containing phosphates, while non-oriented electrical steel employs various coating methods with different thicknesses and ingredients based on end usage and specific user requirements.

 Angle Steel
Angle Steel Channel Steel
Channel Steel Universal Beam (l-Beam)
Universal Beam (l-Beam) H-Beam Steel
H-Beam Steel Galvalume Steel Coil
Galvalume Steel Coil Galvalume Steel Sheet
Galvalume Steel Sheet Galvanized Steel Sheet
Galvanized Steel Sheet Color Coated Plate
Color Coated Plate Stainless Steel Bar
Stainless Steel Bar Stainless Steel Pipe
Stainless Steel Pipe Steel Bar
Steel Bar Wire Rope
Wire Rope Carbon Steel Pipe
Carbon Steel Pipe Carbon Steel Plate
Carbon Steel Plate Aluminum Plate
Aluminum Plate Aluminum Coil
Aluminum Coil Aluminum Pipe
Aluminum Pipe Aluminum Bar
Aluminum Bar Magnesium Ingot
Magnesium Ingot Fasteners
Fasteners