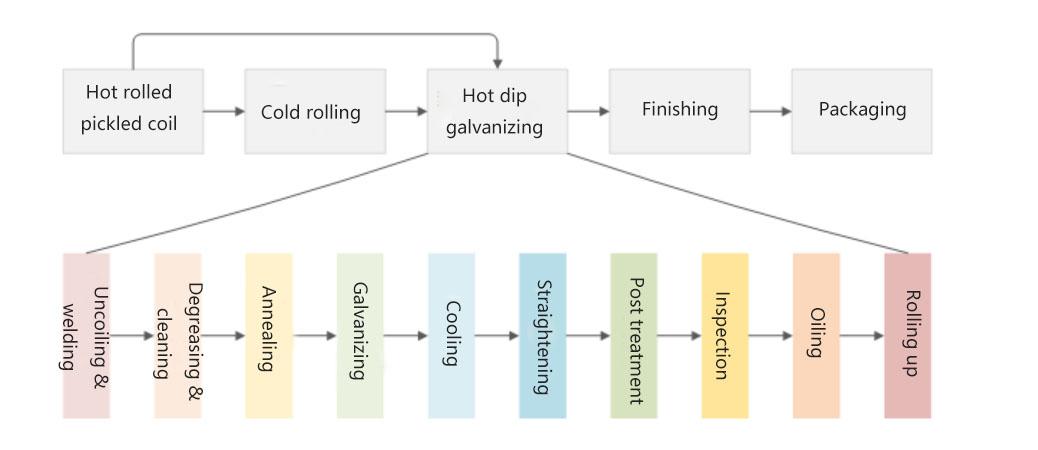
Galvanized Steel Process Introduction Diagram
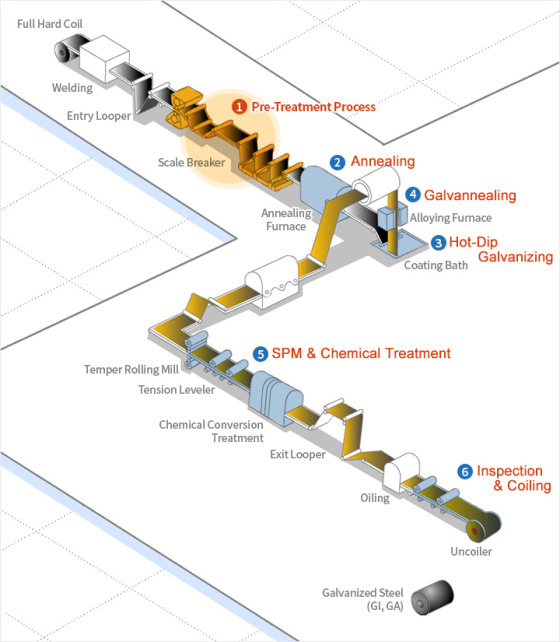
1. Surface treatment: After cold-rolled steel plate processing, the charged steel plate is passed through an alkaline solution, triggering an electrochemical reaction to remove residual rolling oil and other contaminants, thereby cleaning the surface.
2. Annealing: The material properties of pre-treated steel plates are modified and enhanced by recrystallization during the annealing process.
3. Hot-dip galvanizing: After the annealing furnace, the steel plate is immersed in a zinc pot and the surface is covered with molten zinc. The desired coating weight is achieved by using high-pressure air in an air knife to remove excess zinc before curing.
4. Galvanized Annealing: After air knife treatment, the surface of the steel plate can be coated with zinc compounds and then reheated during the annealing process. This allows zinc atoms to diffuse into the iron, forming a zinc-iron alloy.
5. Surface Treatment and Coating: In order to obtain a smooth surface and exquisite finish, the steel plate is machined flat. In addition, in order to prevent the formation of white rust on the surface of active zinc and enhance corrosion resistance, the surface is coated with chromium-free resin.
6. Inspection and Coiling: Steel plates are thoroughly inspected and coiled to ensure quality and prepare them for further processing.

 Angle Steel
Angle Steel Channel Steel
Channel Steel Universal Beam (l-Beam)
Universal Beam (l-Beam) H-Beam Steel
H-Beam Steel Galvalume Steel Coil
Galvalume Steel Coil Galvalume Steel Sheet
Galvalume Steel Sheet Galvanized Steel Sheet
Galvanized Steel Sheet Color Coated Plate
Color Coated Plate Stainless Steel Bar
Stainless Steel Bar Stainless Steel Pipe
Stainless Steel Pipe Steel Bar
Steel Bar Wire Rope
Wire Rope Carbon Steel Pipe
Carbon Steel Pipe Carbon Steel Plate
Carbon Steel Plate Aluminum Plate
Aluminum Plate Aluminum Coil
Aluminum Coil Aluminum Pipe
Aluminum Pipe Aluminum Bar
Aluminum Bar Magnesium Ingot
Magnesium Ingot Fasteners
Fasteners